Product Of Inertia Calculator
Introduction
Calculating the product of inertia is essential in various engineering and physics applications. It helps determine how mass is distributed in a rigid body relative to its axis of rotation. This article provides a simple and accurate calculator along with an explanation of its usage and underlying formula.
How to Use
To use the product of inertia calculator, follow these steps:
- Input the values of mass (m), distance from the x-axis (x), and distance from the y-axis (y).
- Click the “Calculate” button to obtain the result.
Formula
The formula for calculating the product of inertia (Ixy) is given by:
Ixy=∑m×(x×y)
Where:
- m is the mass of each element.
- x is the distance of each element from the x-axis.
- y is the distance of each element from the y-axis.
Example Solve
Suppose we have three masses distributed in a plane:
- Mass 1 (m1) = 2 kg, x1=3 m, y1=1 m
- Mass 2 (m2) = 3 kg, x2=2 m, y2=4 m
- Mass 3 (m3) = 1 kg, x3=5 m, y3=2 m
Using the formula, we can calculate the product of inertia as follows:
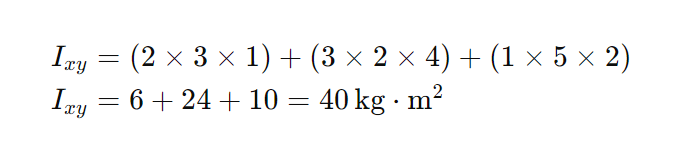
Therefore, the product of inertia (Ixy) for this system is 40 kg·m².
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of the product of inertia?
A: The product of inertia represents how mass is distributed in a rigid body relative to its coordinate axes. It is crucial in analyzing the rotational motion and stability of structures.
Q: Can the product of inertia be negative?
A: Yes, the product of inertia can be negative. It indicates an asymmetric distribution of mass relative to the coordinate axes.
Q: How does the product of inertia differ from the moment of inertia?
A: While the moment of inertia measures an object’s resistance to rotational motion about a specific axis, the product of inertia describes the distribution of mass relative to two perpendicular axes.
Conclusion
The product of inertia calculator provides a convenient tool for engineers and physicists to analyze the distribution of mass in a rigid body. By understanding its usage and formula, users can accurately determine the product of inertia for various applications.