Water Wheel Power Calculator
Introduction
Calculating the power generated by a water wheel is crucial for assessing its efficiency and potential energy production. A water wheel power calculator can simplify this process, allowing users to input relevant parameters and obtain accurate results. In this article, we’ll provide a detailed guide on how to use such a calculator, along with the formula and examples for better understanding.
How to Use
To use the water wheel power calculator, follow these steps:
- Input the required parameters such as water flow rate (Q), water density (ρ), gravitational acceleration (g), and the height from which the water falls (h).
- Click on the “Calculate” button to obtain the power generated by the water wheel.
Formula
The formula to calculate the power generated by a water wheel is:
P=ρ×g×Q×h
Where:
- P is the power generated (in watts).
- ρ is the density of water (in kg/m³).
- g is the gravitational acceleration (approximately 9.81 m/s29.81m/s2).
- Q is the flow rate of water (in cubic meters per second).
- h is the height from which the water falls (in meters).
Example Solve
Let’s consider an example where:
- Water density (ρ) = 1000 kg/m³
- Gravitational acceleration (g) = 9.81 m/s²
- Flow rate (Q) = 0.05 m³/s
- Height (h) = 10 meters
Using the formula:
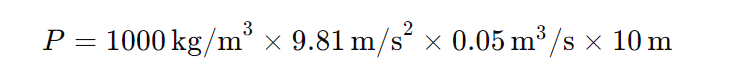
P=4905watts
So, the power generated by the water wheel in this example would be 4905 watts.
FAQs
Q: Can this calculator be used for different units of measurement?
A: Yes, as long as the units are consistent, you can use different units for density, flow rate, and height.
Q: What if the water wheel has mechanical inefficiencies?
A: The calculated power represents the ideal scenario. Mechanical inefficiencies would reduce the actual power output.
Q: How accurate are the results from this calculator?
A: The results are accurate provided the input parameters are measured precisely and the assumptions of the formula hold true.
Conclusion
A water wheel power calculator is a valuable tool for estimating the power generated by a water wheel based on specific parameters. By following the formula and using the calculator, users can gain insights into the potential energy production of water-driven systems.
