Stagnation Enthalpy Calculator
Introduction
In the realm of thermodynamics, understanding stagnation enthalpy is crucial for various engineering applications. Stagnation enthalpy represents the total energy per unit mass of a fluid flowing at a stagnation point, where its velocity becomes zero due to compression or stagnation. Calculating stagnation enthalpy requires precise formulations, which we’ll explore in this article alongside a practical implementation of a calculator.
How to Use
To utilize the stagnation enthalpy calculator, input the necessary parameters such as temperature, pressure, and specific heat ratio, then hit the “Calculate” button to obtain the result.
Formula
The formula to compute stagnation enthalpy (ℎ0h0) is:
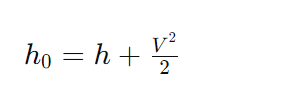
Where:
- h is the enthalpy of the fluid.
- V is the velocity of the fluid at the stagnation point.
Example Solve
Let’s say we have a fluid with an enthalpy (h) of 500 kJ/kg and a velocity (V) of 10 m/s at the stagnation point. Using the formula, we can find the stagnation enthalpy (ℎ0h0):
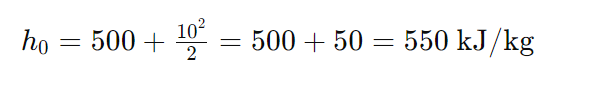
So, the stagnation enthalpy of the fluid is 550 kJ/kg.
FAQ’s
Q: What is stagnation enthalpy?
A: Stagnation enthalpy represents the total energy per unit mass of a fluid at a stagnation point, where its velocity is zero due to compression.
Q: Why is calculating stagnation enthalpy important?
A: Understanding stagnation enthalpy is crucial for various engineering applications, especially in aerodynamics and fluid mechanics, where accurate energy analysis is required.
Q: How does the stagnation enthalpy calculator work?
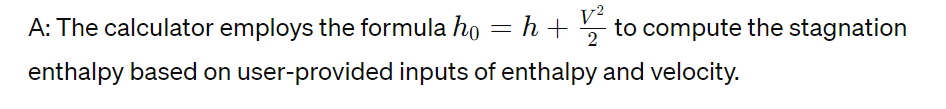
Conclusion
Stagnation enthalpy serves as a fundamental parameter in fluid dynamics, aiding engineers in analyzing fluid behavior and energy distribution. With the help of this calculator and a clear understanding of the formula, precise computations of stagnation enthalpy can be effortlessly performed.
