LMTD Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference Calculator
Calculating the Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) is essential in various engineering applications, particularly in heat exchanger design. An accurate LMTD is crucial for optimizing heat transfer processes.
How to Use
To use the LMTD calculator, follow these simple steps:
- Enter the values for the hot and cold fluid temperatures.
- Specify the respective heat transfer coefficients for both fluids.
- Click the “Calculate” button to obtain the Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference.
Formula
The formula for calculating the Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) is given by:

Where:
- ΔT1 is the temperature difference at one end of the heat exchanger.
- ΔT2 is the temperature difference at the other end of the heat exchanger.
- lnln represents the natural logarithm.
Example Solve
Let’s consider an example:
- ΔT1=100∘C
- ΔT2=60∘C
Assuming these temperature differences, the LMTD can be calculated using the formula mentioned earlier.
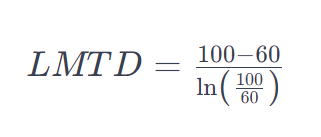
After performing the calculations, the LMTD can be obtained.
FAQs
Q1: Why is LMTD important in heat exchanger design?
LMTD is crucial as it provides a representative temperature difference, aiding in the accurate design and performance assessment of heat exchangers.
Q2: Can the LMTD calculator handle negative temperature differences?
No, the LMTD calculator assumes positive temperature differences as negative values are not physically meaningful in heat exchanger applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) calculator presented here simplifies the process of obtaining this critical parameter for heat exchanger design. By inputting the relevant temperatures and heat transfer coefficients, engineers can efficiently optimize heat transfer processes.
